Difference between revisions of "Brettanomyces and Saccharomyces Co-fermentation"
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
! Technique !! More Funk !! Less Funk !! Note | ! Technique !! More Funk !! Less Funk !! Note | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Inoculation timing || After ''Saccharomyces'' has finished fermentation || At the start of Fermentation || The timing of the ''Brettanomyces'' pitch may not have a significant effect a lot of the time; pending data from George Van Der Merwe or another source of scientific data <ref>[https://www.facebook.com/groups/MilkTheFunk/permalink/2103639509664252/?comment_id=2117621214932748&comment_tracking=%7B%22tn%22%3A%22R%22%7D Richard Preiss. Milk The Funk Facebook thread on co-pitching versus subsequent pitching of ''Brettanomyces''. 06/04/2018.]</ref>. | + | | Inoculation timing || After ''Saccharomyces'' has finished fermentation || At the start of Fermentation || The timing of the ''Brettanomyces'' pitch may not have a significant effect a lot of the time; pending data from George Van Der Merwe or another source of scientific data <ref>[https://www.facebook.com/groups/MilkTheFunk/permalink/2103639509664252/?comment_id=2117621214932748&comment_tracking=%7B%22tn%22%3A%22R%22%7D Richard Preiss. Milk The Funk Facebook thread on co-pitching versus subsequent pitching of ''Brettanomyces''. 06/04/2018.]</ref>. |
|- | |- | ||
| ''Brettanomyces'' Inoculation cell count || Lower cell count or higher cell count || Higher cell count or lower cell count|| Although more data is needed, pitching rate of ''Brettanomyces'' may not have a measured impact on beer flavor. See [[Brettanomyces secondary fermentation experiment]]. | | ''Brettanomyces'' Inoculation cell count || Lower cell count or higher cell count || Higher cell count or lower cell count|| Although more data is needed, pitching rate of ''Brettanomyces'' may not have a measured impact on beer flavor. See [[Brettanomyces secondary fermentation experiment]]. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
See also: | See also: | ||
| + | * [https://www.masterbrewerspodcast.com/062 Interview with Nick Mader on the MBAA podcast.] | ||
* [[Brettanomyces_secondary_fermentation_experiment|''Brettanomyces'' secondary pitch rate experiment by Lance Shaner and Richard Preiss.]] | * [[Brettanomyces_secondary_fermentation_experiment|''Brettanomyces'' secondary pitch rate experiment by Lance Shaner and Richard Preiss.]] | ||
* [[Mixed_Fermentation#Staggered_Versus_Co-Pitching|Mixed Fermentation Staggered vs Co-pitching]]. | * [[Mixed_Fermentation#Staggered_Versus_Co-Pitching|Mixed Fermentation Staggered vs Co-pitching]]. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 60: | ||
==Effects of ''Saccharomyces'' Strain Selection and Staggered vs Co-Pitch== | ==Effects of ''Saccharomyces'' Strain Selection and Staggered vs Co-Pitch== | ||
| − | Anecdotally, brewers often claim that the primary strain of ''S. cerevisiae'' makes a difference when co-fermented with ''Brettanomyces'' | + | Anecdotally, brewers often claim that the primary strain of ''S. cerevisiae'' makes a difference when co-fermented with ''Brettanomyces''. However, until recently, there has been limited scientific analysis to back this claim, and some brewers might disagree with this claim. Similar differences in anecdotal experiences have been shared by brewers in regards to co-pitching ''Saccharomyces'' and ''Brettanomyces'' at the same time, or adding the ''Brettanomyces'' pitch after the ''Saccharomyces'' fermentation has finished (often called a "staggered pitch"). |
===Review of Scientific Analysis=== | ===Review of Scientific Analysis=== | ||
| − | [[File:Tyrawa Fig 15.JPG|thumbnail|250px|right|Figure 15 from [https://atrium.lib.uoguelph.ca/xmlui/handle/10214/14757 Caroline Tyrawa's Masters thesis]. Uploaded with permission from Caroline Tyrawa and Dr. G. van der Merwe's laboratory of Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology.]] | + | [[File:Tyrawa Fig 15.JPG|thumbnail|250px|right|Figure 15 from [https://atrium.lib.uoguelph.ca/xmlui/handle/10214/14757 Caroline Tyrawa's Masters thesis]. Uploaded with permission from Caroline Tyrawa and Dr. G. van der Merwe's laboratory at University of Guelph Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology.]] |
| − | [[File:Tyrawa Fig 19.JPG|thumbnail|250px|right|Figure 19 from [https://atrium.lib.uoguelph.ca/xmlui/handle/10214/14757 Caroline Tyrawa's Masters thesis]. Uploaded with permission from Caroline Tyrawa and Dr. G. van der Merwe's laboratory of Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology.]] | + | [[File:Tyrawa Fig 19.JPG|thumbnail|250px|right|Figure 19 from [https://atrium.lib.uoguelph.ca/xmlui/handle/10214/14757 Caroline Tyrawa's Masters thesis]. Uploaded with permission from Caroline Tyrawa and Dr. G. van der Merwe's laboratory at University of Guelph Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology.]] |
| Line 76: | Line 77: | ||
See also: | See also: | ||
* [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IudVmYyWXss Presentation from Caroline Tyrawa via Escarpment Laboratories Crowdcast video.] | * [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IudVmYyWXss Presentation from Caroline Tyrawa via Escarpment Laboratories Crowdcast video.] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===''Brettanomyces'' Strain Selection=== | ||
| + | [https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/downloads/gh93h631p Riley Humbert's Bachelors thesis] reported that the ability to hyper attenuate beer in secondary fermentation of ''B. bruxellensis'' is strain dependent with some strains fermenting at a slower rate than others (this was also the case for these strains when primary fermenting wort). The fermentation rate did not correlate to phenol production; for example, one strain that produced the most 4-vinyl phenol and 4 ethyl phenol was one of the slowest fermenters. Humbert also reported that strains of ''B. bruxellensis'' isolated from beer performed better than those isolated from wine, which is in agreement with previous experiments <ref>[https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/downloads/gh93h631p Riley Humbert for the degree of Honors Baccalaureate of Science in Chemical Engineering presented on May 21, 2021. Title: Performance of Brettanomyces Yeast Strains in Primary and Secondary Beer Fermentations.]</ref>. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 88: | Line 92: | ||
===External Resources=== | ===External Resources=== | ||
* [https://www.whitelabs.com/sites/default/files/belgianchart_0.pdf White Labs list of Belgian yeast strains and characteristics, including phenols/spiciness.] | * [https://www.whitelabs.com/sites/default/files/belgianchart_0.pdf White Labs list of Belgian yeast strains and characteristics, including phenols/spiciness.] | ||
| + | * [https://beerandbrewing.com/podcast-episode-253-matt-van-wyk-and-brian-coombs-of-alesong-brewing-and-blending/ Craft Beer & Brewing Podcast Episode 253: Matt Van Wyk and Brian Coombs of Alesong (52 mins in).] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:07, 19 September 2022
Brettanomyces and Saccharomyces Co-fermentation, for the purposes of this article, is a type of mixed fermentation that specifically refers to fermentations that contain Saccharomyces and Brettanomyces. They do not contain significant amounts of lactic acid produced by lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus and Pediococcus). As such, these beers may have a lightly tart flavor from acetic acid production by Brettanomyces, but are generally not described as being sour if properly brewed (see the Mixed Fermentation page for mixed fermentation sour beers). The flavor of beers fermented with Saccharomyces (generally ale yeast, but they can also be fermented with lager yeast) and Brettanomyces is often dominated by the array of flavor compounds produced by Brettanomyces, unless the beer is young in which case the ester and phenol profile of the fermenting strain of Saccharomyces might still have an impact on the flavor. In the case of young beers, the flavor profile will begin to be changed by Brettanomyces as esters, phenols, and fatty acids are created and metabolized.
Generically speaking, these flavors almost always consist of both fruity esters and phenolic components. Sometimes they also consist of an array of other flavors that are generically described as "funky". Specifically, fruity esters range from tropical fruits to stone fruits to citrus fruits, and are produced by all strains of Brettanomyces to some degree. Phenols, fatty acids, alcohols, aldehydes, and other compounds can also create a wide range of flavors including smoke, "barnyard animal", horse blanket, sweat, body odor, rancid cheese, etc. For more information on the identification of these compounds and the known conditions that impact their production, see Brettanomyces metabolism. For 100% Brettanomyces beers, see 100% Brettanomyces Fermentation.
Contents
Brewing Methods
| Technique | More Funk | Less Funk | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculation timing | After Saccharomyces has finished fermentation | At the start of Fermentation | The timing of the Brettanomyces pitch may not have a significant effect a lot of the time; pending data from George Van Der Merwe or another source of scientific data [1]. |
| Brettanomyces Inoculation cell count | Lower cell count or higher cell count | Higher cell count or lower cell count | Although more data is needed, pitching rate of Brettanomyces may not have a measured impact on beer flavor. See Brettanomyces secondary fermentation experiment. |
| Strain of Saccharomyces | Phenol positive strain | Phenol negative strain | POF+ strains of S. cerevisiae form 4-vinylguaiacol by enzymatic decarboxylation of ferulic acid [2]. More recent data suggests that POF+ strains of Saccharomyces are not necessary for Brettanomyces to create phenols because Brettanomyces can create the precursor 4-vinyl phenols on its own as long as ferulic acid and other grain derived precursors are available [3]. See Brettanomyces secondary fermentation experiment and this The Mad Fermentationist blog article. |
| Ferulic Acid (malt derived) | More Ferulic Acid | Less Ferulic Acid | A precursor of 4-vinylguaiacol. Perform a ferulic acid rest, and use around 70% barley malt and 30% wheat malt for the highest ferulic acid extraction (see Brettanomyces phenol production for more information). |
| Time since Inoculation | Aged Beer | Young Beer | |
| Fermentation Temperature | Higher temperature increases esters in some but not all strains of B. bruxellensis. | Lower temperature decreases esters in some but not all strains of B. bruxellensis. | Temperature does not appear to significantly affect the amount of phenol compounds produced by B. bruxellensis in a 100% Brettanomyces fermentation. Therefore, the perception of a more "funky" beer might depend on producing less esters rather than creating more phenols. See Brettanomyces phenols and 100% Brettanomyces Fermentation for more information. |
Aging and Packaging
In general, beers brewed with Saccharomyces and Brettanomyces tend to lead to a slow fermentation by the Brettanomyces, which can hyper-attenuate the beer over time (see Brettanomyces carbohydrate metabolism. These beers are often aged for at least 3-4 months to wait for a stable final gravity before packaging. However, they can also be aged for longer which helps develop flavors produced by the Brettanomyces. Due to the potential for acetic acid development when exposed to oxygen over time, care should be taken when aging any beer with living Brettanomyces (see mixed fermentation aging).
See the Packaging page for instructions on determining when it is safe to package a Brettanomyces and Saccharomyces Co-fermentation, and tips on how to package it.
Dosing Clean Beer with Brettanomyces At Bottling
One method that some brewers attempt is adding a small pitch of Brettanomyces to a clean beer at bottling time. This can be done either in the bottling bucket/tank, or added to each bottle individually. If adding Brettanomyces to each bottle individually, a 1 mL dosage of Brettanomyces from a starter should be enough since pitching rate seems to have little impact on the beer [4]. Some brewers believe that adding the Brettanomyces at bottling time results in a more complex beer. It is speculated that the extra stress of pressure within the bottles helps to create this complexity, although evidence for this is lacking. Other stressors such as lack of oxygen are also speculated to have an impact.
One challenge with this approach is that it is difficult to predict how much Brettanomyces will further attenuate the beer once in the bottle. Over-carbonation and bottle bombs can easily be an issue with this method if the brewer is not careful. Each degree Plato adds ~2 volumes of CO2 [5]. Since different species and strains of Brettanomyces ferment different types of sugars, some strains might be safer for dosing at bottling time. For example, most strains of B. anomulus do not ferment maltose, which is around 50% of sugar in wort, so this makes it a good choice for adding to the beer at bottling. However, if the amount of additional attenuation is already known for a particular beer and a particular strain of Brettanomyces, than any strain can be used.
Daniel Addey-Jibb, co-owner and brewer at Le Castor near Montreal, Quebec advises that the approach that his brewery takes is to ferment their saison wort down to 1°P. Once at 1°P , the beer is cold crashed, fined, and then bottled with Brettanomyces. The beer is then stored at room temperature for three months to condition naturally in the bottle. During bottling conditioning, their Brettanomyces culture takes the beer down below 0°P, and their desired level of carbonation is reached. This process took Addey-Jibb's team dozens of trials to perfect using their specific wort recipe, saison yeast, and Brettanomyces strain. Different species or strains of Brettanomyces might ferment differently, and different wort compositions might also ferment differently. For example, Addey-Jibb's saison is mashed with malted barley, wheat, and rye at a low temperature so there are not many higher chain sugars, allowing the beer to dry out quickly [6]. Other wort compositions that include higher chain sugars from specialty malts and/or higher mashing temperatures might ferment much slower, and thus knowing what the final gravity will be once Brettanomyces is added is difficult to know without running trials on that specific fermentation profile. It is recommended to use Belgian beer bottles of sparkling wine bottles that can withstand higher pressures than regular beer bottles just in case over-carbonation becomes an issue.
A "forced fermentation test" might help to determine the final gravity of a given Brettanomyces strain or blend of strains. Use the same wort composition as the beer in question, and pitch a large cell count of Brettanomyces. Use a stirplate if possible, and an airlock to keep oxygen out (some Brettanomyces strains can attenuate further when fermented aerobically and thus will not give an accurate final gravity reading when fermented aerobically). Keep the temperature around 80-85°F for a month or two, and then measure the gravity. Each gravity point gives produces about 0.5 volumes of CO2. Adjust the priming sugar for the rest of the batch accordingly. Use bottles that are rated for higher pressures, such as Belgian bottles or sparkling wine bottles [7].
For more information on bottling sour and funky beer in general, see the Packaging page.
Effects of Brettanomyces Pitching Rate
Review of Scientific Analysis
The published analysis of beer that is co-fermented with S. cerevisiae and Brettanomyces is rare. In this section, published data on this topic will be reviewed.
Nick Mader of Fremont Brewing (2017 Master Brewers Conference Presentation) compared various flavor compounds produced between a 100% S. cerevisiae (BSI-565, Wallionian Saison yeast) and 100% B. bruxellensis (BSI-Drei), and percentage combinations of 75/25, 50/50, and 25/75 inoculations of the BSI-565 strain and BSI-Drei strain. Fermentations were completed in 35 days, and the beers were analyzed for their ester and phenol content. Attenuation results were about the same for the 100% BSI-565 and the co-fermentation of BSI-565 and BSI-Drei, while the attenuation rate was around 12% lower for the 100% BSI-Drei fermentation, indicating that co-fermentation with these two particular strains did not greatly affect attenuation and that the BSI-Drei did not ferment as well by itself.
The esters that were analyzed were ethyl acetate (pineapple, pear, solventy), ethyl butyrate (tropical fruit), ethyl hexanoate (apple), ethyl decanoate (apple, brandy), ethyl octanoate (waxy, pineapple), isoamyl acetate (banana), isobutyl alcohol (solventy), and isoamyl alcohol (fusel, banana). Ethyl acetate had the most sporadic results. It was highest in the 100% BSI-565 fermentation (43 ppm; above the 33 ppm odor threshold), and lowest in the 100% BSI-Drei fermentation (21 ppm; below the 33 ppm odor threshold), but when co-fermented the ethyl acetate production rates formed a pattern of more ethyl acetate as the pitching rate of BSI-565 was decreased and the pitching rate of BSI-Drei was increased. The 75/25 ratio produced 27 ppm of ethyl acetate, 50/50 produced 34 ppm, and the 25/75 produced 42 ppm (BSI-565 to BSI-Drei ratio in percent pitching rate). The highest ethyl acetate concentrations were therefore for the 100% BSI-565 and the 25%/75% BSI-565 to BSI-Drei.
Ethyl butyrate was highest in the 100% BSI-565, and curved downward as the pitching rate for the BSI-565 strain was decreased. Ethyl butyrate was below the odor threshold in the 100% BSI-Drei fermentation. This indicates that the production of ethyl butyrate was dependent on the pitching rate of BSI-565, and that the BSI-Drei strain did not produce significant amounts of this ester. For each of the esters ethyl hexanoate, ethyl decanoate, ethyl octanoate, they had a slight decrease as the pitching rate of BSI-565 decreased, indicating that these esters are produced more by the BSI-565 strain; however, the small measured differences may not be reflected in the actual taste/aroma of the beers since the differences were so small. The exception was ethyl decanoate which was around 3x higher in the 100% BSI-Drei, which indicates that ethyl decanoate is a major flavor contributor to 100% BSI-Drei fermentations. Overall, the ester concentrations were significantly lower in the BSI-565/BSI-Drei fermentations compared to the strains of S. cerevisiae and B. bruxellensis used by Lance Shaner and Richard Preiss in their similar experiment, indicating that total ester concentrations are highly dependent on the strains used. Isoamyl acetate, which was above odor threshold in the 100% BSI-565 fermentation, was almost not detectable in any of the fermentations that contained BSI-Drei (it was 0 ppm in the 100% BSI-Drei fermentation), which is in agreement with other studies that Brettanomyces hydrolyzes this ester. The alcohols isobutyl alcohol and isoamyl alcohol were slightly decreased as the pitching rate of BSI-565 decreased, and were extremely low in the 100% BSI-Drei, indicating that these alcohols were produced more so by BSI-565.
The phenols that were measured in Mader's experiment were 4-vinylguaiacol (clove), 4-ethylguaiacol (smokey, spicy), and 4-ethylphenol (medicinal, barnyard). While the 100% BSI-565 fermentation had high levels of 4-VG (1800 ppm), they were less than half the amount in the co-fermented ferments (600-800 ppm) but still above odor threshold (300 ppm) (the different ratios of BSI-565 to BSI-Drei did not have a large impact), and 4-VG was below threshold in the 100% BSI-Drei fermentation. 4-EG and 4-EP had high levels in the co-fermentations with BSI-565 and BSI-Drei and the 100% BSI-Drei, and the ratios did not have a large impact. This is in agreement with another experiment by Lance Shaner and Richard Preiss that showed that pitching rate of Brettanomyces after fermentation with S. cerevisiae did not have a great effect on the levels of phenols produced [8].
See also:
- Interview with Nick Mader on the MBAA podcast.
- Brettanomyces secondary pitch rate experiment by Lance Shaner and Richard Preiss.
- Mixed Fermentation Staggered vs Co-pitching.
- Effects of Lactobacillus on co-fermentation.
Effects of Saccharomyces Strain Selection and Staggered vs Co-Pitch
Anecdotally, brewers often claim that the primary strain of S. cerevisiae makes a difference when co-fermented with Brettanomyces. However, until recently, there has been limited scientific analysis to back this claim, and some brewers might disagree with this claim. Similar differences in anecdotal experiences have been shared by brewers in regards to co-pitching Saccharomyces and Brettanomyces at the same time, or adding the Brettanomyces pitch after the Saccharomyces fermentation has finished (often called a "staggered pitch").
Review of Scientific Analysis

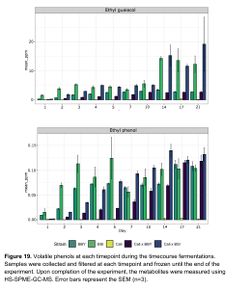
According to Caroline Tyrawa's masters thesis, some of the flavor impacts of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation can remain intact despite the flavor impacts of a subsequent Brettanomyces bruxellensis fermentation. This indicates that the strain selection for S. cerevisiae in a co-fermentation with B. bruxellensis can make a difference to the final product. Tyrawa tested the fermentation of three different strains of S. cerevisiae and three different strains of B. bruxellensis. The strains of S. cerevisiae were the Cal Ale strain (neutral), the Vermont Ale strain (fruity), and the St. Remy Belgian strain (phenolic). The three B. bruxellensis strains were the BSI Drei strain, a strain isolated from a winery, and a strain isolated from a brewery. The B. bruxellensis strains were selected for their desirable flavor impact in beer as well as their ability to ferment the sugars present in wort. Each of the 6 strains were given a primary-only fermentation. In addition, for each of the S. cerevisiae strains, they were also co-fermented in combination with each of the B. bruxellensis strains pitched at one time (a total of 9 combinations). Another set of co-fermentations were done by allowing the S. cerevisiae strains to ferment for 7 days before adding the B. bruxellensis strains (staggered pitches). The fermentations were analyzed during a total of 21 days at 22°C. The rate of sugar fermentation was measured, as well as analysis of key flavor compounds [9].
The primary fermentations consumed the wort sugars as would be predicted, with the S. cerevisiae strains completing fermentation in 5 days, and the Brettanomyces strains reaching a similar level of attenuation after a 1-2 day lag phase but at a slower rate which continued during all 21 days and probably continuing past 21 days if they were allowed to continue fermentation. For the staggered pitches, the S. cerevisiae strains appeared to be finished with their fermentation by the time the B. bruxellensis strains were pitched on day 7. After a day or two of lag, the B. bruxellensis strains slowly continued to attenuate the wort over the next 14 days and did not taper off at the end of the additional 14 days (21 days total counting the initial S. cerevisiae fermentation), indicating that attenuation by the B. bruxellensis strains may not have been finished. For the staggered co-pitches, the highest fermentation rate was achieved with the all three of the B. bruxellensis strains that were co-fermented with the St. Remy Belgian strain and the lowest fermentation rate was with the Cal Ale strain, indicating that the strain choice of S. cerevisiae affects the fermentation rate over time in combination with the strain of B. bruxellensis. The specific combination of B. bruxellensis strain and S. cerevisiae strain can have different effects on fermentation rate as well. For the Cal Ale and Vermont Ale strains, the wine strain of B. bruxellensis fermented the most efficiently, while the BSI Drei strain fermented most efficiently in combination with the St. Remy Belgian strain. The author did not speculate on why this might be the case. Interestingly, the set of fermentations where both the S. cerevisiae and B. bruxellensis were inoculated at the same time did not have this effect. These co-fermentations where the strains were pitched at the same time there looked much like the primary fermentation of the S. cerevisiae strains where the fermentations were mostly done after 5-6 days with no noticeable attenuation after this short time. This data indicates that higher and slower attenuation occurs when Brettanomyces is inoculated after the primary S. cerevisiae fermentation has finished, but not when S. cerevisiae and B. bruxellensis are inoculated at the same time [9].
Key flavor compounds were analyzed for the different fermentations. Overall, the results showed that some flavor compounds produced by S. cerevisiae remained even when co-fermented with Brettanomyces (either co-pitched, or staggered pitch), indicating that the strain selection for S. cerevisiae for a co-fermentation remains important for the final flavor profile of the beer (see Figure 15). It is also possible that since this experiment was only conducted for 21 days that the Brettanomyces did not have enough time to have its full flavor impact. In general, there were no significant flavor differences between the co-pitched fermentations versus the staggered pitch fermentations (despite there being a very significant attenuation difference as previously mentioned) [9].
The ester profiles of the co-fermentations (both the staggered and co-pitch) were a little bit subdued compared to the primary fermentations with Brettanomyces, indicating that primary fermentations with Brettanomyces produces higher amounts of esters versus co-fermentation of Brettanomyces with S. cerevisiae. For example, lower levels of ethyl caproate, ethyl butyrate, ethyl caprylate, ethyl decanoate, ethyl nonanoate, and ethyl lactate, were seen in the co-fermentations versus the Brettanomyces primary fermentations with some of these compounds dropping below flavor threshold levels (ethyl caproate, for example). The ester production of Brettanomyces peaked at 14 days, and then esters slowly degraded. In the co-fermentations, the Brettanomyces appeared to be degrading acetate esters produced by the S. cerevisiae, such as phenyl ethyl acetate, and producing higher amounts of of ethyl acetate. Phenol production began as soon as Brettanomyces was pitched, and this has been hypothesized to play a large role in replenishing NAD+ to alleviate the initial lag growth phase in Brettanomyces. Interestingly, levels of 4-ethylphenol were produced at a faster rate in the 100% Brettanomyces fermentations, but by the end of the 21 day trial period the the 100% Brettanomyces ferments had slightly lower concentrations of 4-EP versus the co-fermentations with S. cerevisiae, indicating that perhaps 100% Brettanomyces fermentations produce more phenols up front, but after some time of aging co-fermentations can produce slightly higher levels of phenols (see Figure 19) [9].
See also:
Brettanomyces Strain Selection
Riley Humbert's Bachelors thesis reported that the ability to hyper attenuate beer in secondary fermentation of B. bruxellensis is strain dependent with some strains fermenting at a slower rate than others (this was also the case for these strains when primary fermenting wort). The fermentation rate did not correlate to phenol production; for example, one strain that produced the most 4-vinyl phenol and 4 ethyl phenol was one of the slowest fermenters. Humbert also reported that strains of B. bruxellensis isolated from beer performed better than those isolated from wine, which is in agreement with previous experiments [10].
See Also
Additional Articles on MTF Wiki
- 100% Brettanomyces Fermentation
- Mixed Fermentation
- Brettanomyces
- Saccharomyces
- Mixed Cultures
- Brettanomyces secondary fermentation experiment
External Resources
- White Labs list of Belgian yeast strains and characteristics, including phenols/spiciness.
- Craft Beer & Brewing Podcast Episode 253: Matt Van Wyk and Brian Coombs of Alesong (52 mins in).
References
- ↑ Richard Preiss. Milk The Funk Facebook thread on co-pitching versus subsequent pitching of Brettanomyces. 06/04/2018.
- ↑ Coghe, S., Benoot, K., Delvaux, F., Vanderhaegen, B., & Delvaux, F. R. (2004). Ferulic acid release and 4-vinylguaiacol formation during brewing and fermentation: indications for feruloyl esterase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52(3), 602-608.
- ↑ Conversation with Richard Preiss on MTF. 02/16/2017.
- ↑ Brettanomyces_secondary_fermentation_experiment
- ↑ "Accurately Calculating Sugar Additions for Carbonation." Kai Troester. Braukaiser.com. Retrieved 08/07/2016.
- ↑ Addey-Jibb, Daniel. Interview on the Brewing Network's Session podcast. 10/04/2016.
- ↑ Conversation with Adi Hastings on MTF regarding forced fermentation tests with Brettanomyces. 1/2/2017.
- ↑ Nick Mader. 2017 Master Brewers Conference Presentation. 2017.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Demystifying Brettanomyces bruxellensis: Fermentation kinetics, flavour compound production, and nutrient requirements during wort fermentation. University of Guelph, Masters Thesis. Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2020.
- ↑ Riley Humbert for the degree of Honors Baccalaureate of Science in Chemical Engineering presented on May 21, 2021. Title: Performance of Brettanomyces Yeast Strains in Primary and Secondary Beer Fermentations.