Difference between revisions of "Mold"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Preventing Mold Growth=== | ===Preventing Mold Growth=== | ||
| − | * If aging sour beer on whole fruit, use a punch-down tool frequently so that the alcohol and low pH kills any mold that might be present before it begins to grow. | + | * If aging sour beer on whole fruit, use a punch-down tool frequently so that the alcohol and low pH kills any mold that might be present before it begins to grow. Homebrewers can gently swirl their carboys to accomplish the same thing. |
* Limit oxygen exposure to the beer. | * Limit oxygen exposure to the beer. | ||
* Use diligent sanitation practices. | * Use diligent sanitation practices. | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 15 July 2016
(In progress)
Mold or mould are multicellular fungi that grow in the form of filaments called hyphae that appear like long branch-like structures under a microscope. Although not a taxonomic designation, there are an estimaged 10,000 - 300,000 of species of molds that live in a wide variety of environments [1]. In general they cause biodegredation of foods and other natural materials (such as wood in buildings), which has a wide role of effects depending on the species of mold. For example, some species of mold can be the cause of food spoilage, and other species play an important role in food production such as in cheese and soy sauce production [2]. Certain species of mold are thought to contribute precursors that effect flavor production in the toasting of oak barrels [3] Molds have also been used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce antibiotics and other medicines. Certain molds can cause allergic reactions as well as diseases from mold growth within the body or from mycotoxin production in exposed foods or from breathing spores from mold growth in buildings [2].
Contents
Mold in Beer and Health Concerns
Mold Growth in Beer
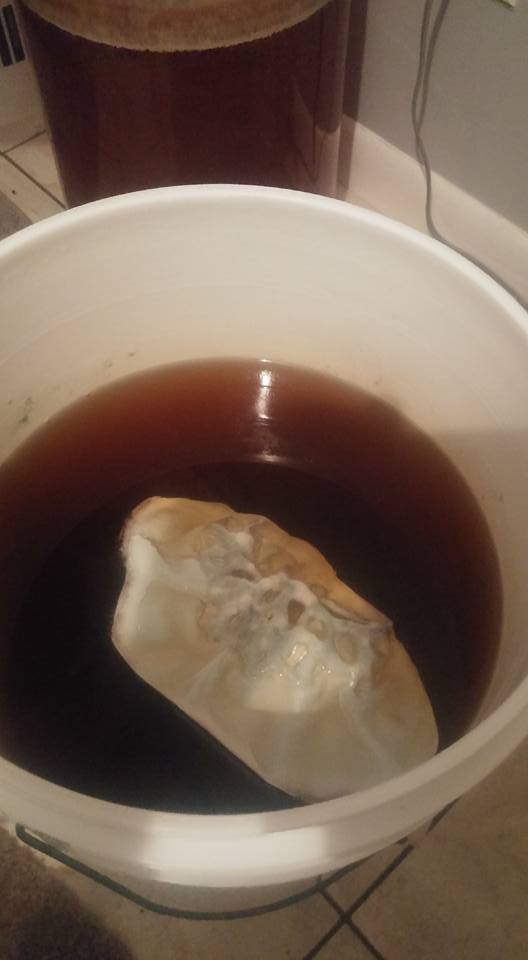
Although little studying has been done on mold growth in beer, it has been known to occur in barrel aged beers are fruited sour beers. Oxygen needs to be present in order for mold to grow. Mold growth on fruit that is in sour beer can occur if the fruit is floating above the surface of the beer, and enough oxygen is present (either from vacuum suck-back, oxygen permeability of the vessel, or sampling). For this reason, many commercial sour brewers will "punch down" the fruit frequently with a dish-like tool.
Preventing Mold Growth
- If aging sour beer on whole fruit, use a punch-down tool frequently so that the alcohol and low pH kills any mold that might be present before it begins to grow. Homebrewers can gently swirl their carboys to accomplish the same thing.
- Limit oxygen exposure to the beer.
- Use diligent sanitation practices.
- Inspect barrels for mold prior to use; discard barrels that have mold growth, or disassemble the barrel and vigorously clean/sanitize the wood before use. See the Barrel page for details on storing and maintaining barrels.
Health Concerns
A small number of molds can produce mycotoxins, which are poisonous substances, or aflatoxins, which are cancer-causing poisons. Some molds that do not produce toxins can still cause allergic reactions or respiratory problems [1]. Their effects can be accumulative, rather than immediately toxic as in the case of pathogenic bacteria. As a general rule of thumb, pigmented molds (non-white/grey) are more likely to produce poisonous substances, however there are exceptions to this rule [4].
Identifying mold based on what it looks like is not a reliable way to determine if a mold is a cause of concern for health (need ref). If mold is present in beer, it might be possible for commercial breweries to remove the mold and send it to a lab to check if it is a toxic mold before allowing the beer to be consumed (need ref). Some homebrewers may decide to risk taking a chance that the mold will not cause illness, however we recommend discarding beer that has come into contact with mold, especially if serving to others (mold growing on SOFT fruits and vegetables with high moisture content can be contaminated below the surface [1]).
See the USDA website for more information on the health concerns of mold that grows on food.
Identifying Mold
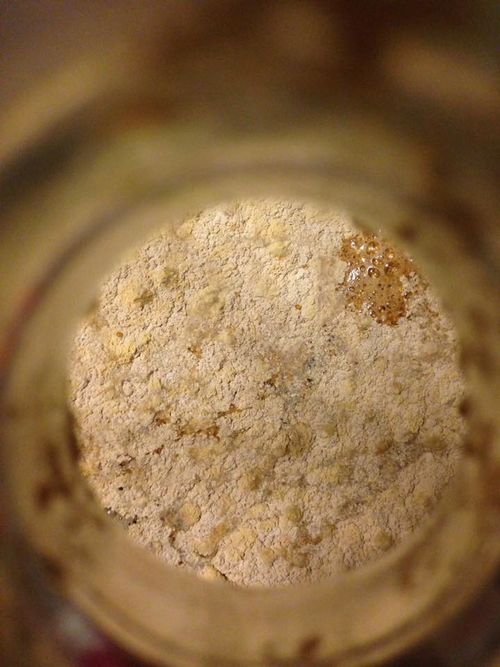
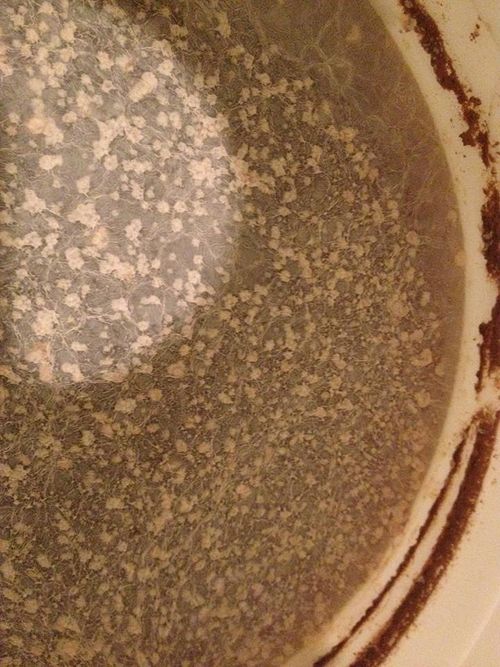
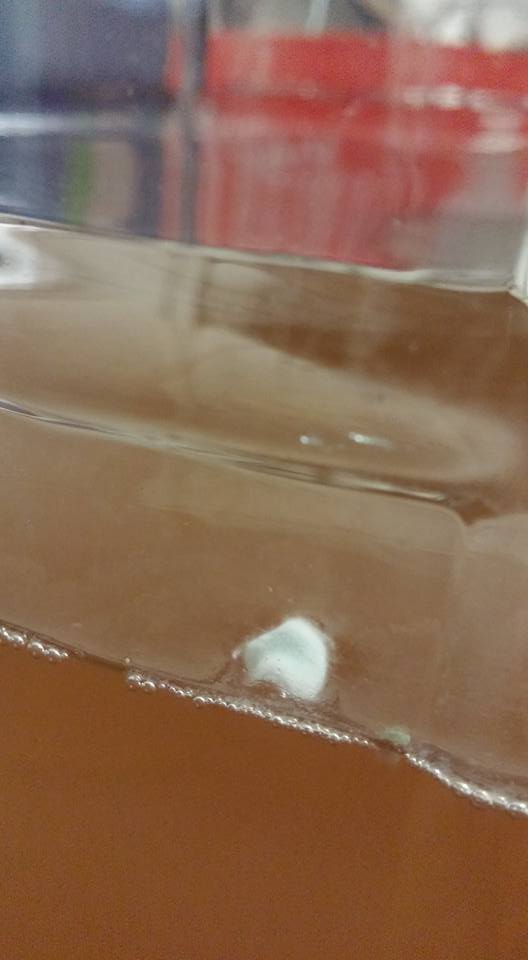
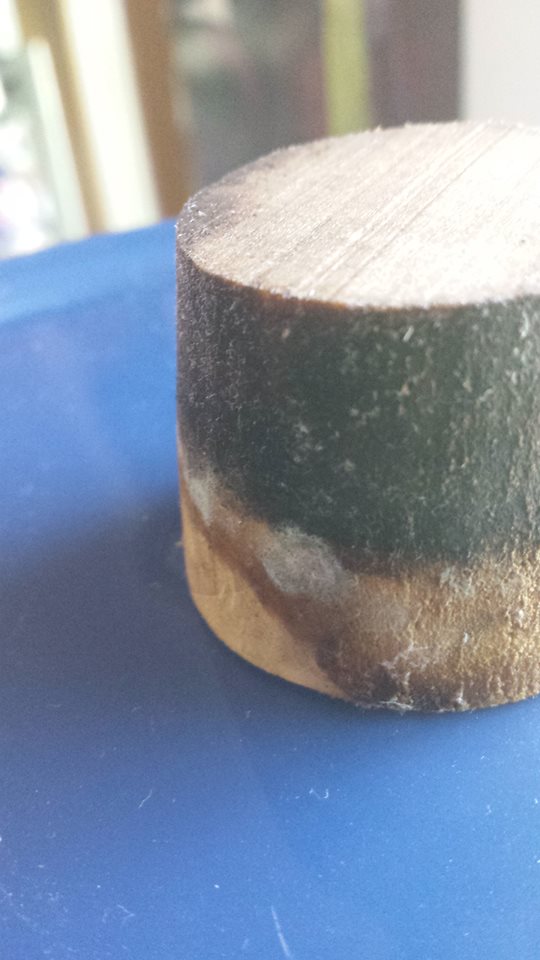
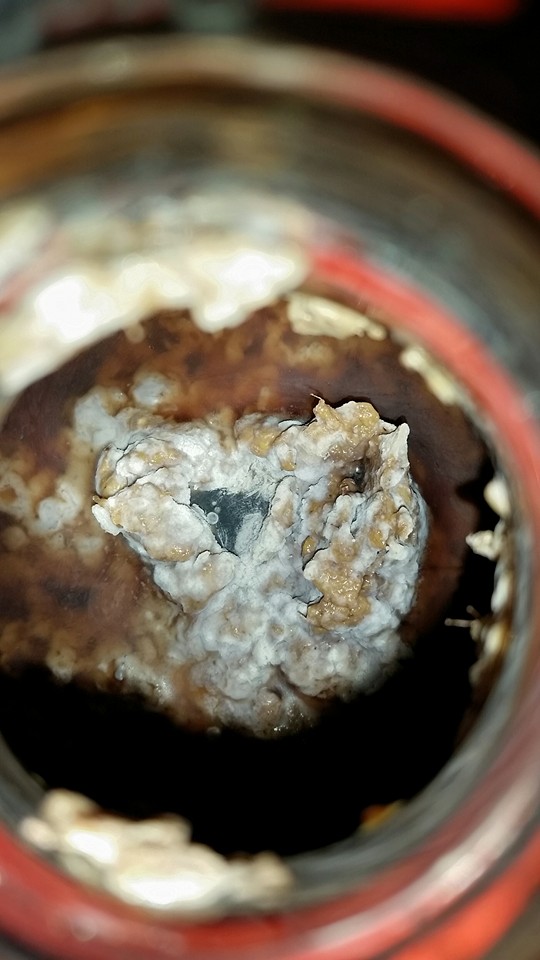
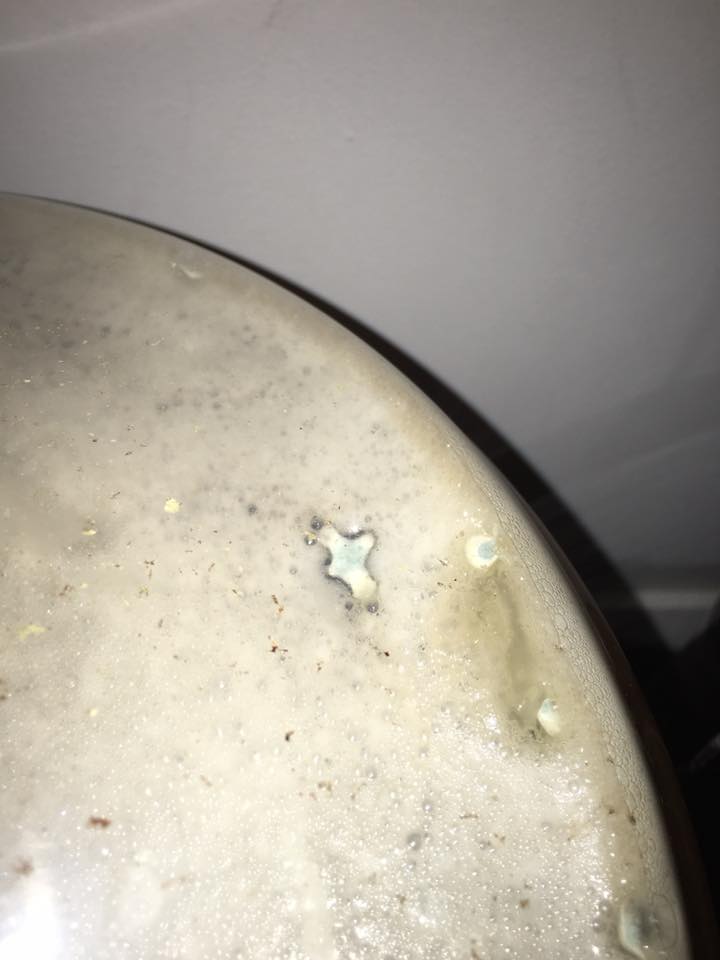
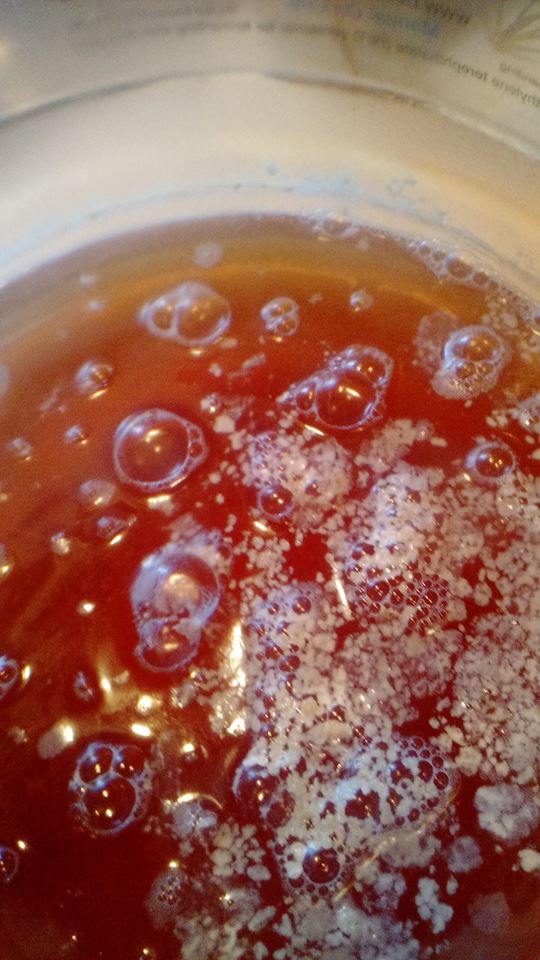
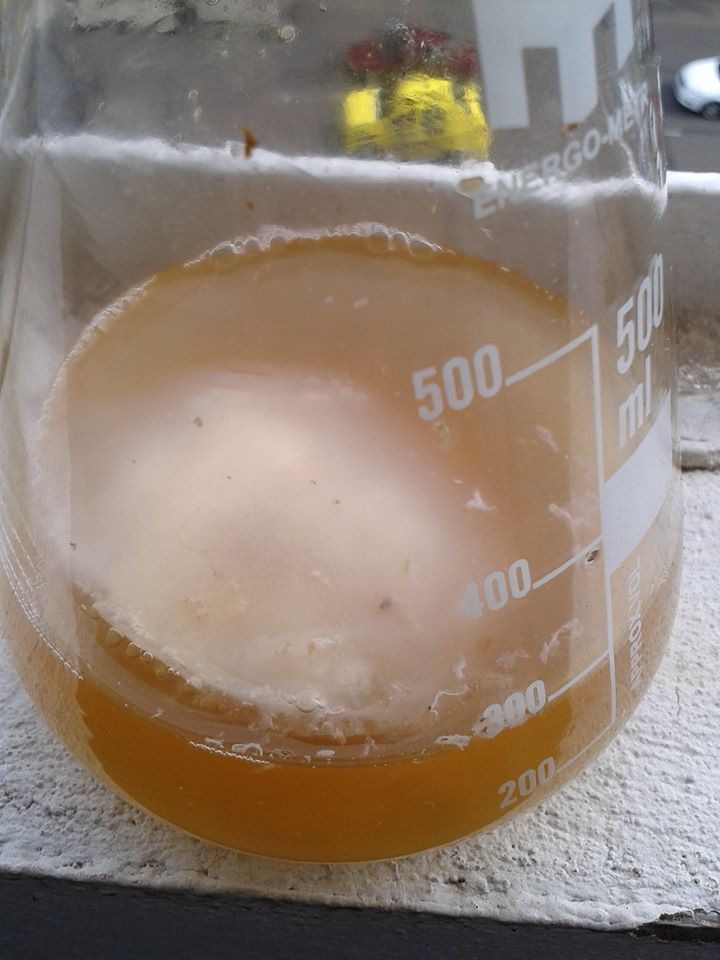
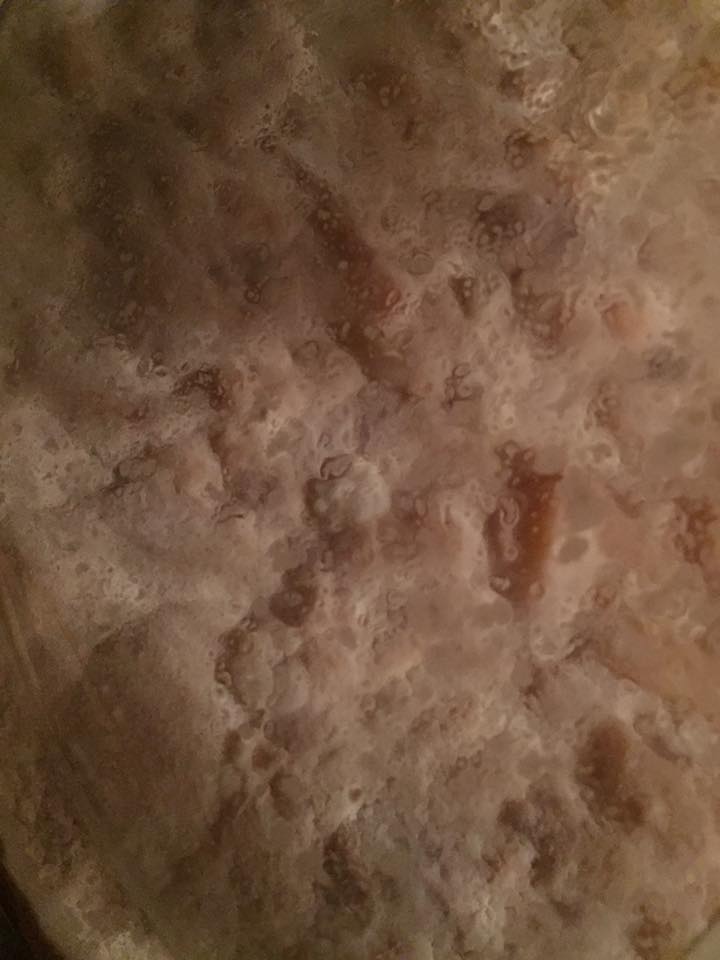
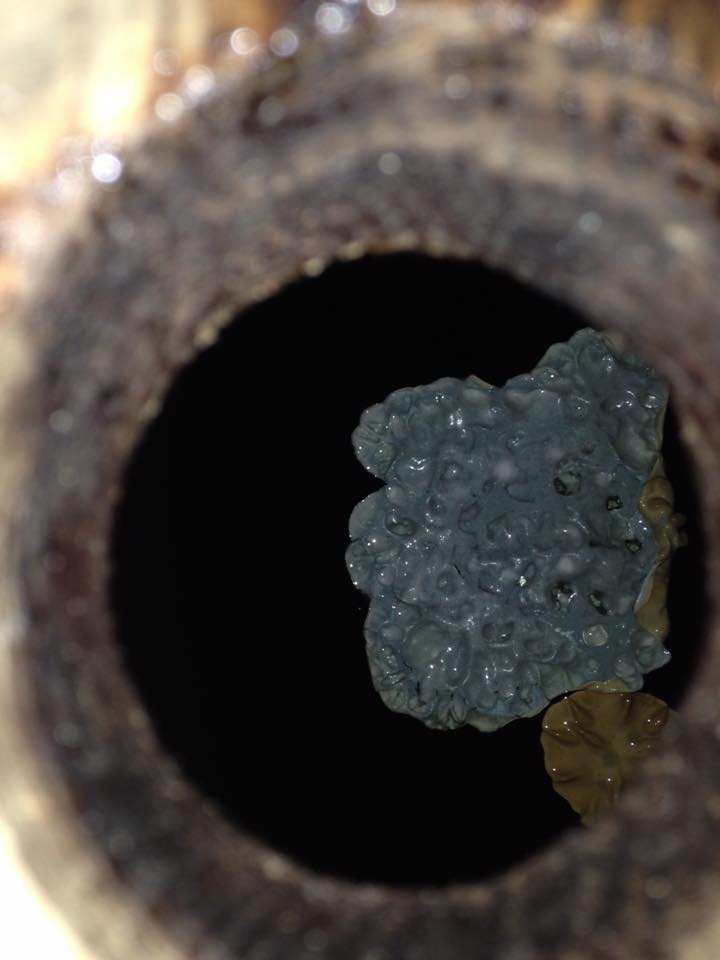
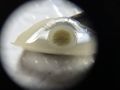
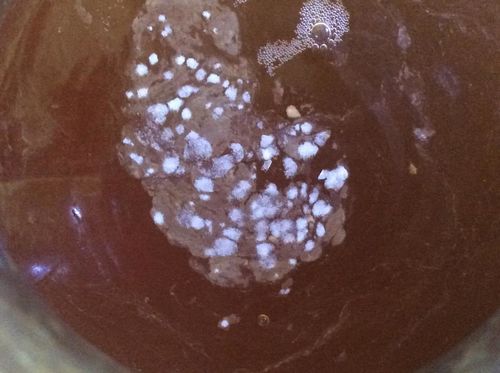
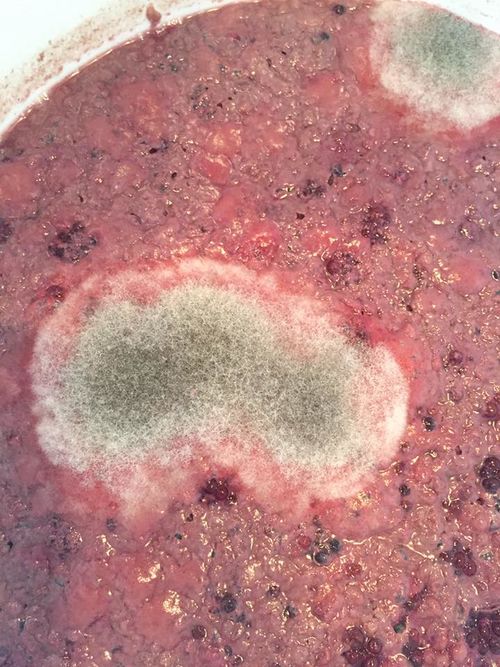
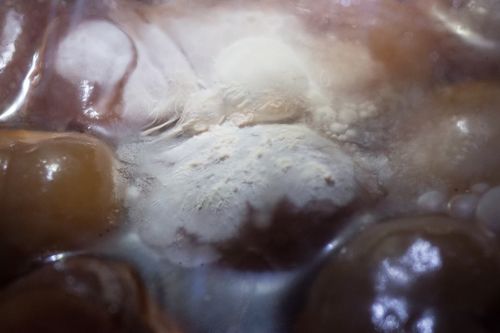
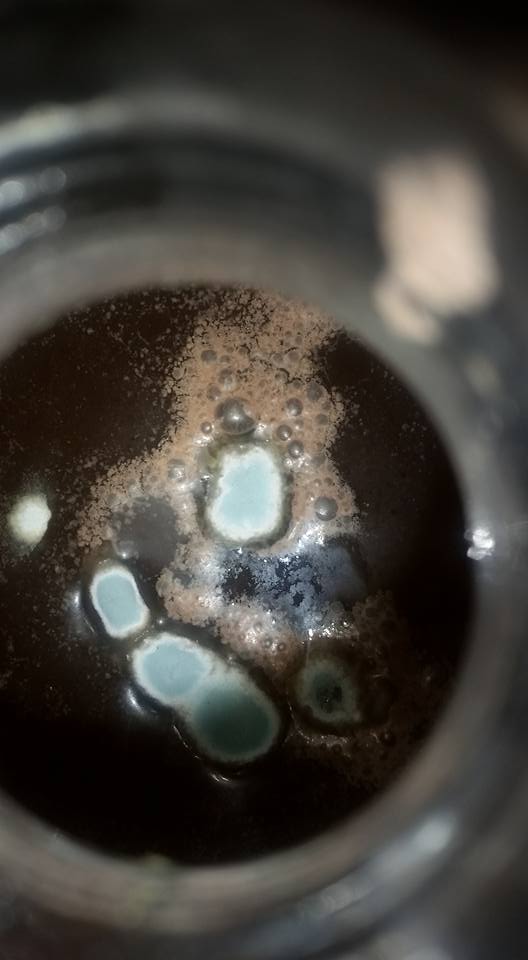
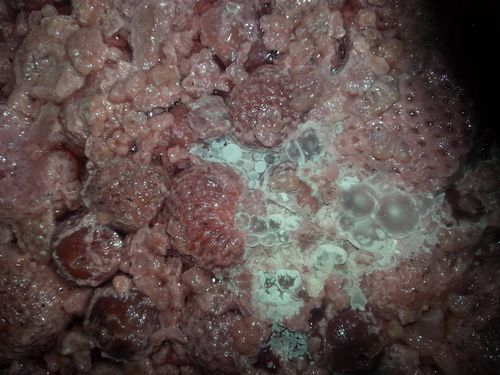
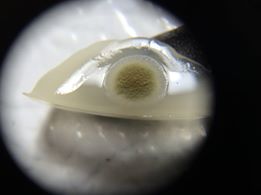
As mentioned above, identifying the species of mold based on what it looks like with the naked eye is not a reliable way to identify it at the species level, and thus not a reliable way to know if the mold growth is safe. It is, however, usually easy to tell the difference between general mold growth and pellicle or yeast growth. We recommend taking a picture through a hand lens when posting an image of what might be mold as this will make it easier to identify. See the images below for examples.
Mold vs Pellicle Examples
The following table shows examples of mold or pellicles from the Milk The Funk Facebook group, and the consensus on whether mold is likely present or not based on the image.
See Also
Additional Articles on MTF Wiki
External Resources
- USDA Website on Molds.
- "Bacteriological Analytical Manual; Chapter 18; Yeasts, Molds and Mycotoxins."; FDA Website.
- Causes of Food Poisoning. Mayo Clinic website. 07/24/2014. Retrieved .07/12/2016.]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Molds On Food: Are They Dangerous?" United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 07/15/2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mold. Wikipedia. Retrieved 07/12/2016.
- ↑ The duration effect of natural seasoning of Quercus petraea Liebl. and Quercus robur L. on the diversity of existing fungi flora and some aspects of its ecology. N. Vivas. 1996.
- ↑ Conversation with Bryan of Sui Generis Blog on MTF. 04/20/2016.