Brettanomyces and Saccharomyces Co-fermentation
Funky mixed fermentations, for the purposes of this article, refer to fermentations that contain Saccharomyces and Brettanomyces. They do not contain lactic acid bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Pediococcus. As such, these beers may have a lightly tart flavor, but are generally not described as being sour (see the Mixed Fermentation page). The flavor of beers fermented with Saccharomyces (generally ale yeast, but they can also be fermented with lager yeast) and Brettanomyces is often dominated by the array of flavor compounds produced by Brettanomyces, unless the beer is young in which case the ester and phenol profile of the fermenting strain of Saccharomyces might still have an impact on flavor. In the case of young beers, the flavor profile will begin to be changed by Brettanomyces as esters, phenols, and fatty acids are created and metabolized.
Generically speaking, these flavors almost always consist of both fruity esters and phenolic components. Sometimes they also consist of an array of other flavors that are generically described as "funky". Specifically, fruity esters range from tropical fruits to stone fruits, and are produced by all strains of Brettanomyces to some degree. Phenols, fatty acids, alcohols, aldehydes, and other compounds can also create a wide range of flavors including smoke, "barnyard animal", bitterness that lingers on the palate longer than hop bitterness, horse blanket, sweat, body odor, rancid cheese, etc. For more information on the identification of these compounds and the known conditions that impact their production, see Brettanomyces metabolism. For 100% Brettanomyces beers, see 100% Brettanomyces Fermentation.
Contents
Brewing Methods
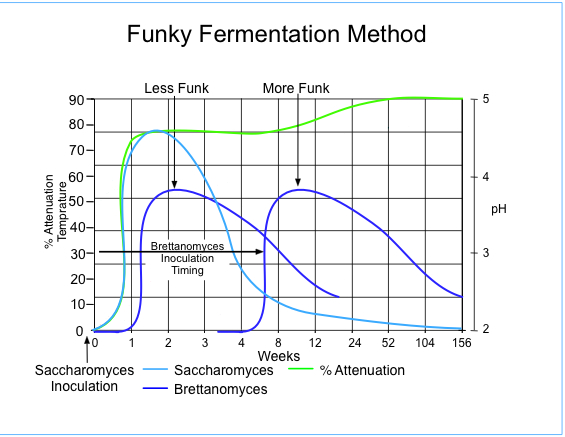
| Technique | More Funk | Less Funk | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculation timing | After Saccharomyces has finished fermentation | At the start of Fermentation | See figure 1 |
| Brettanomyces Inoculation cell count | Lower cell count or higher cell count | Higher cell count or lower cell count | Although more data is needed, pitching rate of Brettanomyces may not have a measured impact on beer flavor. See Brettanomyces secondary fermentation experiment. |
| Strain of Saccharomyces | Phenol positive strain | Phenol negative strain | POF+ strains of S. cerevisiae form 4-vinylguaiacol by enzymatic decarboxylation of ferulic acid [2]. More recent data suggests that POF+ strains of Saccharomyces are not necessary for Brettanomyces to create phenols because Brettanomyces can create the precursor 4-vinyl phenols on its own as long as ferulic acid and other grain derived percursors are available [3]. See Brettanomyces secondary fermentation experiment. |
| Ferulic Acid (malt derived) | More Ferulic Acid | Less Ferulic Acid | A precursor of 4-vinylguaiacol. Perform a ferulic acid rest, and use grains that contain more ferulic acid such as wheat. |
| Time since Inoculation | Aged Beer | Young Beer | |
| Fermentation Temperature | Higher temperature increases esters in some but not all strains of B. bruxellensis. | Lower temperature decreases esters in some but not all strains of B. bruxellensis. | Temperature does not appear to affect the amount of phenol compounds produced by B. bruxellensis in a 100% Brettanomyces fermentation. Therefore, the perception of a more "funky" beer might depend on producing less esters rather than creating more phenols. See Brettanomyces phenols and 100% Brettanomyces Fermentation for more information. |
Finishing Funky Mixed Fermentations
Bottling and Kegging
See the Packaging page.
Dosing Clean Beer with Brettanomyces At Bottling
One method that some brewers attempt is adding a small pitch of Brettanomyces to a clean beer at bottling time. This can be done either in the bottling bucket/tank, or added to each bottle individually. If adding Brettanomyces to each bottle individually, a 1 mL dosage of Brettanomyces from a starter should be enough since pitching rate seems to have little impact on the beer [4]. Some brewers believe that adding the Brettanomyces at bottling time results in a more complex beer. It is speculated that the extra stress of pressure within the bottles helps to create this complexity.
One challenge with this approach is that it is difficult to predict how much Brettanomyces will further attenuate the beer once in the bottle. Over-carbonation and bottle bombs can easily be an issue with this method if the brewer is not careful. Each degree Plato adds ~2 volumes of CO2 [5]. Daniel Addey-Jibb, co-owner and brewer at Le Castor near Montreal, Quebec advises that the approach that his brewery takes is to ferment their saison wort down to 1°P. Once at 1°P , the beer is cold crashed, fined, and then bottled with Brettanomyces. The beer is then stored at room temperature for three months to condition naturally in the bottle. During bottling conditioning, their Brettanomyces culture takes the beer down below 0°P, and their desired level of carbonation is reached. This process took Addey-Jibb's team dozens of trials to perfect using their specific wort recipe, saison yeast, and Brettanomyces strain. Different species or strains of Brettanomyces might ferment differently, and different wort compositions might also ferment differently. For example, Addey-Jibb's saison is mashed with malted barley, wheat, and rye at a low temperature so there are not many higher chain sugars, allowing the beer to dry out quickly [6]. Other wort compositions that include higher chain sugars from specialty malts and/or higher mashing temperatures might ferment much slower, and thus knowing what the final gravity will be once Brettanomyces is added is difficult to know without running trials on that specific fermentation profile.
A "forced fermentation test" might help to determine the final gravity of a given Brettanomyces strain or blend of strains. Use the same wort composition as the beer in question, and pitch a large cell count of Brettanomyces. Use a stirplate if possible, and an airlock to keep oxygen out (some Brettanomyces strains can attenuate further when fermented aerobically and thus will not give an accurate final gravity reading when fermented aerobically). Keep the temperature around 80-85°F for a month or two, and then measure the gravity. Each gravity point gives produces about 0.5 volumes of CO2. Adjust the priming sugar for the rest of the batch accordingly. Use bottles that are rated for higher pressures, such as Belgian bottles or sparkling wine bottles [7].
For more information on bottling sour and funky beer in general, see the Packaging page.
See Also
Additional Articles on MTF Wiki
External Resources
References
- ↑ Tonsmeire, M. (2014). American Sour Beers. Brewers Publications
- ↑ Coghe, S., Benoot, K., Delvaux, F., Vanderhaegen, B., & Delvaux, F. R. (2004). Ferulic acid release and 4-vinylguaiacol formation during brewing and fermentation: indications for feruloyl esterase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52(3), 602-608.
- ↑ Conversation with Richard Preiss on MTF. 02/16/2017.
- ↑ Brettanomyces_secondary_fermentation_experiment
- ↑ "Accurately Calculating Sugar Additions for Carbonation." Kai Troester. Braukaiser.com. Retrieved 08/07/2016.
- ↑ Addey-Jibb, Daniel. Interview on the Brewing Network's Session podcast. 10/04/2016.
- ↑ Conversation with Adi Hastings on MTF regarding forced fermentation tests with Brettanomyces. 1/2/2017.